Your basket is currently empty!
Understanding Cryptocurrency Staking: A Beginner’s Guide and Technical Deep Dive
Key Points
- What It Is: Staking involves locking up cryptocurrency to support a blockchain’s operations, earning rewards in return, similar to earning interest on a savings account.
- How It Works: Users stake coins to help validate transactions on Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains, with rewards varying by network and stake size.
- Benefits: Offers passive income, supports network security, and is energy-efficient compared to mining.
- Risks: Includes lockup periods, potential slashing (loss of staked coins), and platform risks, so research is essential.
- Getting Started: Requires owning a PoS cryptocurrency and choosing a staking method (solo, pool, or exchange).
What Is Staking?
Staking is a way to earn rewards by holding and locking up your cryptocurrency to help a blockchain network run securely. It’s like putting money in a savings account, where the bank pays you interest for keeping your funds there. In staking, you contribute to the network’s security and get paid in more cryptocurrency.
How Does It Work?
In Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains, like Ethereum or Cardano, staking means locking up your coins to support the network’s operations, such as validating transactions. You can stake directly as a validator or delegate your coins to someone else who validates on your behalf. In return, you earn rewards, typically paid in the same cryptocurrency.
Why Stake?
Staking lets you earn passive income without selling your crypto, helps secure the blockchain, and is more environmentally friendly than traditional mining. However, it’s important to understand the risks, like locked funds or potential penalties, and choose a reliable platform.

Understanding Cryptocurrency Staking: A Beginner’s Guide and Technical Deep Dive
Cryptocurrency staking has become a popular way for users to earn rewards while contributing to the security and functionality of blockchain networks. Whether you’re new to crypto or a seasoned enthusiast, understanding staking is essential. This blog post explains staking in two parts: a beginner-friendly section for those just starting out and a technical deep dive for those who want to explore the mechanics in greater detail.
Part 1: Staking for Dummies – What Is It and How Does It Work?
What Is Staking?
Imagine you have some money in a savings account, and the bank pays you interest for keeping it there. Staking is similar, but instead of money in a bank, you’re using cryptocurrency to help secure a blockchain network. In return, you earn more cryptocurrency as rewards.
A blockchain is like a digital ledger that records all transactions on a network. To keep this ledger secure and accurate, cryptocurrencies use different methods. One of these is Proof-of-Stake (PoS), where users “stake” their cryptocurrency to participate in validating transactions and creating new blocks on the blockchain. Popular PoS blockchains include Ethereum, Cardano, and Solana.
How Does Staking Work?
When you stake your cryptocurrency, you lock it up for a period to help the network operate securely. This locked crypto is used to select validators, who are responsible for verifying transactions and adding them to the blockchain. In return, validators (or those who delegate to them) earn rewards in the form of additional cryptocurrency.
Here’s a simple step-by-step process:
- Buy Stakeable Crypto: Purchase a cryptocurrency that supports staking, such as Ethereum (ETH), Cardano (ADA), or Solana (SOL).
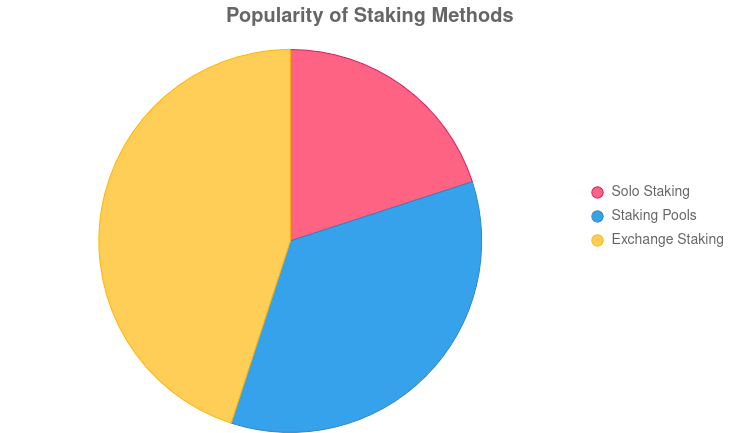
- Choose a Staking Method:
- Solo Staking: Run your own validator node, which requires technical knowledge and a significant amount of crypto.
- Staking Pools: Join a group of users to combine your stake, making it easier to participate.
- Exchanges: Use platforms like Coinbase or Binance, which handle staking for you.
- Lock Your Crypto: Stake your coins through a wallet or platform, either by locking them directly or delegating them to a validator.
- Earn Rewards: Rewards are distributed periodically (e.g., daily, weekly, or monthly), depending on the blockchain and platform.
Not all cryptocurrencies support staking—only those using PoS allow it. For example, Bitcoin uses Proof-of-Work (PoW), which relies on mining, not staking.
Benefits of Staking
- Earn Passive Income: Staking lets you grow your crypto holdings without selling them, with annual yields often exceeding 11% for some assets, according to Staking Rewards.
- Support Network Security: Your staked crypto helps ensure the blockchain runs smoothly and securely.
- Energy Efficiency: PoS is far more environmentally friendly than PoW, which requires significant computing power.
Risks and Considerations
- Lockup Periods: Staked crypto may be locked for a set time, meaning you can’t access it immediately. For example, Ethereum staking may require a waiting period for withdrawals.
- Slashing: If a validator acts dishonestly or fails to perform (e.g., goes offline), they may lose part of their staked crypto, a penalty called slashing.
- Platform Risks: Using third-party platforms like exchanges or staking pools introduces risks like hacking or platform failure. Always choose reputable services.
- Market Volatility: Rewards are paid in crypto, so their value in dollars can fluctuate with market prices.
Getting Started with Staking
- Research Stakeable Cryptocurrencies: Check which coins support staking. Common options include Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, Avalanche, and Polkadot.
- Acquire Crypto: Buy your chosen cryptocurrency on exchanges like Coinbase or Binance.
- Select a Staking Platform:
- Wallets: Use wallets like MetaMask or Trust Wallet for delegated staking.
- Exchanges: Platforms like Coinbase or Kraken offer user-friendly staking options.
- Staking Pools: Services like BlockDaemon or MyContainer help maximize rewards.
- Understand Terms: Check lockup periods, reward rates, and fees (e.g., pool commissions, typically 5–15%).
- Start Staking: Follow the platform’s instructions to stake or delegate your crypto.
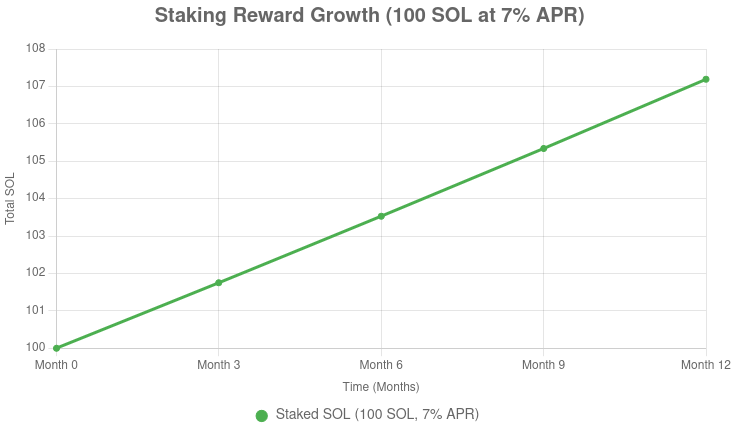
Example: If you stake 100 SOL (Solana) worth ~$15,000 at a 7% annual yield, you could earn ~7 SOL per year (~$1,050), minus any fees, assuming stable prices.
| Staking Method | Pros | Cons | Example Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solo Staking | Full control, higher rewards | High technical requirements, large stake needed | Ethereum (32 ETH minimum) |
| Staking Pools | Lower entry barrier, shared rewards | Pool fees, counterparty risk | BlockDaemon, MyContainer |
| Exchange Staking | Easy to use, no technical setup | Higher fees, less control | Coinbase, Binance |
Part 2: Technical Deep Dive into Staking
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Consensus Mechanism
PoS is a consensus mechanism where validators are chosen to create and validate blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake. Unlike PoW, which relies on computational power, PoS uses economic incentives to secure the network. The probability of being selected as a validator is proportional to the stake, often combined with randomization and staking duration to ensure fairness.
Key features of PoS:
- Validator Selection: Weighted by stake size, duration, and randomness algorithms.
- Energy Efficiency: Requires minimal computational resources compared to PoW.
- Security: Staked coins act as collateral, discouraging malicious behavior.
Validator Responsibilities
Validators in a PoS network:
- Propose Blocks: Create new blocks containing transactions to add to the blockchain.
- Validate Transactions: Verify the legitimacy of transactions in proposed blocks.
- Maintain Network Integrity: Ensure uptime and adherence to protocol rules to avoid penalties.
To become a validator, users typically need a minimum stake (e.g., 32 ETH for Ethereum) and must run a node with high uptime and security.
Staking Pools and Delegation
For users with smaller stakes or limited technical expertise, staking pools and delegation offer accessible alternatives:
- Staking Pools: Users combine their stakes into a pool managed by a validator, sharing rewards proportional to their contribution, minus fees (typically 5–15%).
- Delegation: Users assign their stake’s voting power to a validator without transferring ownership, maintaining liquidity in some cases.
For example, on Cardano, users can delegate ADA to a stake pool via wallets like Daedalus, earning rewards without running a node.
Smart Contracts in Staking
Staking often involves smart contracts, self-executing programs on the blockchain that automate staking processes. For instance:
- Ethereum Staking Contract: Ethereum’s Beacon Chain uses a smart contract to manage staked ETH, validator registration, and reward distribution. Users deposit 32 ETH into the contract to become validators.
- Delegation Contracts: Pools use smart contracts to define terms, such as reward distribution and fees.
Example (simplified Ethereum staking contract in Solidity):
contract Staking {
mapping(address => uint256) public stakes;
function stake() public payable {
stakes[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
function distributeRewards(address validator, uint256 reward) internal {
// Logic to distribute rewards to stakers
}
}Reward Calculation
Rewards depend on several factors:
- Stake Size: Larger stakes increase the likelihood of being selected as a validator.
- Network Parameters: Total staked coins, block rewards, and transaction fees.
- Validator Performance: Uptime and correct validation maximize rewards.
- Inflation Rate: Some networks mint new coins, affecting reward rates.
Formula (simplified):
Reward = (User’s Stake / Total Network Stake) × Block Rewards × (1 - Pool Fee)For example, if 1 billion SOL is staked network-wide, and you stake 100 SOL, with a block reward of 1,000 SOL per period and a 10% pool fee, your reward is:
(100 / 1,000,000,000) × 1,000 × 0.9 = 0.00009 SOL per periodAnnual Percentage Rate (APR) varies, with Staking Rewards reporting averages above 11% for top PoS assets.
Security and Risks
- Slashing: Validators face penalties for misbehavior, such as double-signing or downtime. For example, Ethereum may slash up to 100% of a validator’s stake for severe violations.
- Centralization Risk: If a few validators control most staked coins, the network may become less decentralized.
- Technical Risks: Smart contract bugs or platform hacks can lead to losses.
- Market Volatility: Rewards are paid in crypto, so their fiat value fluctuates.
Advanced Staking Strategies
- Liquid Staking: Platforms like Lido (Lido) allow users to stake ETH and receive stETH, a liquid token usable in DeFi while earning staking rewards. This maintains liquidity without sacrificing rewards.
- Governance Participation: Some PoS networks, like Polkadot, allow stakers to vote on protocol upgrades, giving them influence over network development.
- Multi-Chain Staking: Diversify stakes across multiple PoS networks to spread risk and optimize returns.
Example: Staking on Ethereum
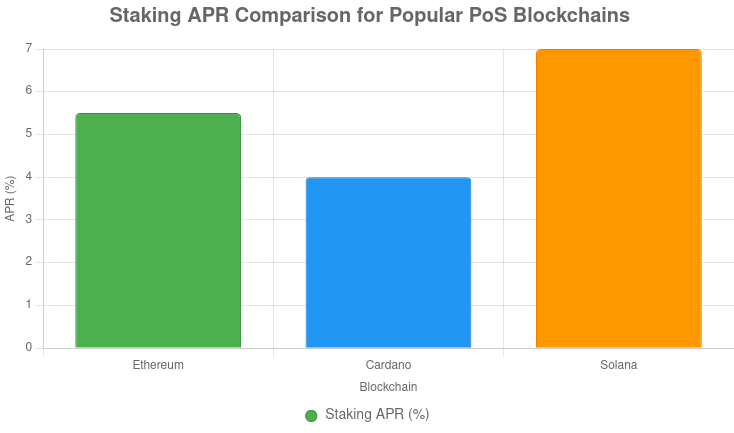
Ethereum’s PoS, introduced with the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade (now fully integrated post-Merge), requires validators to stake 32 ETH (~$45,000 as of September 2022). Users deposit ETH into a staking contract on the Beacon Chain, which manages validator duties. Rewards come from transaction fees and newly minted ETH, typically yielding 4–7% APR.
For smaller stakeholders, services like Lido allow staking any amount of ETH, issuing stETH in return. The Shanghai upgrade (2023) enabled withdrawals, reducing lockup risks. Users can stake via exchanges like Coinbase or wallets like MetaMask.
| Blockchain | Minimum Stake | Typical APR | Lockup Period | Example Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum | 32 ETH | 4–7% | Variable | Lido, Coinbase |
| Cardano | None | 3–5% | None (delegation) | Daedalus, Yoroi |
| Solana | None | 6–8% | ~2 days | Phantom, Kraken |
Conclusion
Staking is a powerful way to earn passive income while supporting blockchain networks. For beginners, it’s a straightforward process to start earning rewards, but choosing a reliable platform and understanding lockup periods are key. For technical users, mastering PoS mechanics, validator roles, and advanced strategies like liquid staking can optimize returns. Always research the specific blockchain, platform, and risks before staking to ensure a secure and rewarding experience.
